Data binding is about connecting the view (the HTML) to the model, which is stored in $scope variable that is passed as an argument to the controller function in our javascript file. There are two things that can happen in data binding:
- Changes in the view trigger changes in the model.
- Changes in the model trigger changes in the view.
View to Model Data Binding
In general, the user will change the view by interacting with input elements. If we want an input element to update the model, we need to use the ng-model directive (a custom attribute) as shown below. The value assigned to this directive should map to a variable name that has been added to the controller’s $scope variable.
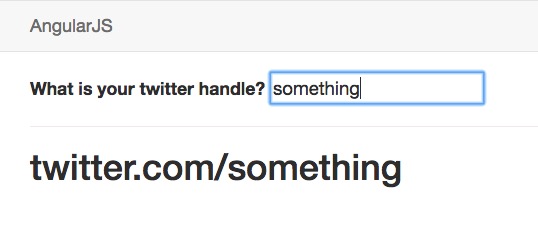
This code shows an input element with binding to a handle variable:
<div class="container">
<div ng-controller="mainController">
<div>
<label>What is your twitter handle?</label>
<input type="text" ng-model="handle" />
</div>
<hr />
<h1>twitter.com/{{ lowercasehandle() }}</h1>
</div>
</div>
The corresponding controller is setup as follows:
var myApp = angular.module('myApp', []);
myApp.controller('mainController', ['$scope', '$filter', function($scope, $filter) {
$scope.handle = '';
$scope.lowercasehandle = function() {
return $filter('lowercase')($scope.handle);
};
}]);
Text entered in the input element will update the handle variable in the model automatically.
Model to View Data Binding
Binding from the model to the view is accomplished through interpolation, which involves inserting strings from the model into the HTML. Interpolation is done through a double set of curly braces as highlighted here:
<div class="container">
<div ng-controller="mainController">
<div>
<label>What is your twitter handle?</label>
<input type="text" ng-model="handle" />
</div>
<hr />
<h1>twitter.com/{{ lowercasehandle() }}</h1>
</div>
</div>
Angular looks for the highlighted function in the $scope variable. The function itself was added to the scope within the controller function as highlighted here:
var myApp = angular.module('myApp', []);
myApp.controller('mainController', ['$scope', '$filter', function($scope, $filter) {
$scope.handle = '';
$scope.lowercasehandle = function() {
return $filter('lowercase')($scope.handle);
};
}]);
The lowercasehandle() function will be evaluated any time there is a change detected in the model, so the model effectively updates the view.
By combining both forms of data binding we make the input element update the model and the model in turn will update the h1 element automatically.
The component that handles all these data binding operations is the scope, which automatically deploys event listeners and implements a digest loop that evaluates changes. If for some reason there is a change that takes place outside the angular scope which changes the model, we can force the change to trigger a digest cycle through the $apply function of $scope.
https://docs.angularjs.org/api/ng/type/$rootScope.Scope